This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Reference
1 - T-SQL
The query editor supports the use of T-SQL in addition to its primary query language, Kusto query language (KQL). While KQL is the recommended query language, T-SQL can be useful for tools that are unable to use KQL.
Query with T-SQL
To run a T-SQL query, begin the query with an empty T-SQL comment line: --. The -- syntax tells the query editor to interpret the following query as T-SQL and not KQL.
Example
--
SELECT * FROM StormEvents
T-SQL to Kusto Query Language
The query editor supports the ability to translate T-SQL queries into KQL. This translation feature can be helpful for users who are familiar with SQL and want to learn more about KQL.
To get the equivalent KQL for a T-SQL SELECT statement, add the keyword explain before the query. The output will be the KQL version of the query, which can be useful for understanding the corresponding KQL syntax and concepts.
Remember to preface T-SQL queries with a T-SQL comment line, --, to tell the query editor to interpret the following query as T-SQL and not KQL.
Example
--
explain
SELECT top(10) *
FROM StormEvents
ORDER BY DamageProperty DESC
Output
StormEvents
| project
StartTime,
EndTime,
EpisodeId,
EventId,
State,
EventType,
InjuriesDirect,
InjuriesIndirect,
DeathsDirect,
DeathsIndirect,
DamageProperty,
DamageCrops,
Source,
BeginLocation,
EndLocation,
BeginLat,
BeginLon,
EndLat,
EndLon,
EpisodeNarrative,
EventNarrative,
StormSummary
| sort by DamageProperty desc nulls first
| take int(10)
Run stored functions
When using T-SQL, we recommend that you create optimized KQL queries and encapsulate them in stored functions, as doing so minimizes T-SQL code and may increase performance. For example, if you have a stored function as described in the following table, you can execute it as shown in the code example.
| Name | Parameters | Body | Folder | DocString |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyFunction | (myLimit: long) | {StormEvents | take myLimit} | MyFolder | Demo function with parameter |
SELECT * FROM kusto.MyFunction(10)
Set request properties
Request properties control how a query executes and returns results. To set request properties with T-SQL, preface your query with one or more statements with the following syntax:
Syntax
DECLARE @__kql_set_requestPropertyName type = value;
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| requestPropertyName | string | ✔️ | The name of the request property to set. |
| type | string | ✔️ | The T-SQL data type of the value. |
| value | scalar | ✔️ | The value to assign to the request property. |
Examples
The following table shows examples for how to set request properties with T-SQL.
| Request property | Example |
|---|---|
query_datetimescope_to | DECLARE @__kql_set_query_datetimescope_to DATETIME = ‘2023-03-31 03:02:01’; |
request_app_name | DECLARE @__kql_set_request_app_name NVARCHAR = ‘kuku’; |
query_results_cache_max_age | DECLARE @__kql_set_query_results_cache_max_age TIME = ‘00:05:00’; |
truncationmaxsize | DECLARE @__kql_set_truncationmaxsize BIGINT = 4294967297; |
maxoutputcolumns | DECLARE @__kql_set_maxoutputcolumns INT = 3001; |
notruncation | DECLARE @__kql_set_notruncation BIT = 1; |
norequesttimeout | DECLARE @__kql_set_norequesttimeout BIT = 0; |
To set request properties with KQL, see set statement.
Coverage
The query environment offers limited support for T-SQL. The following table outlines the T-SQL statements and features that aren’t supported or are partially supported.
| T-SQL statement or feature | Description |
|---|---|
CREATE, INSERT, DROP, and ALTER | Not supported |
| Schema or data modifications | Not supported |
ANY, ALL, and EXISTS | Not supported |
WITHIN GROUP | Not supported |
TOP PERCENT | Not supported |
TOP WITH TIES | Evaluated as regular TOP |
TRUNCATE | Returns the nearest value |
SELECT * | Column order may differ from expectation. Use column names if order matters. |
AT TIME ZONE | Not supported |
| SQL cursors | Not supported |
| Correlated subqueries | Not supported |
| Recursive CTEs | Not supported |
| Dynamic statements | Not supported |
| Flow control statements | Only IF THEN ELSE statements with an identical schema for THEN and ELSE are supported. |
| Duplicate column names | Not supported. The original name is preserved for one column. |
| Data types | Data returned may differ in type from SQL Server. For example, TINYINT and SMALLINT have no equivalent in Kusto, and may return as INT32 or INT64 instead of BYTE or INT16. |
Related content
- Learn about SQL Server emulation in Azure Data Explorer
- Use the SQL to Kusto Query Language cheat sheet
2 - JSONPath syntax
JSONPath notation describes the path to one or more elements in a JSON document.
The JSONPath notation is used in the following scenarios:
- To specify data mappings for ingestion
- To specify data mappings for external tables
- In Kusto Query Language (KQL) functions that process dynamic objects, like bag_remove_keys() and extract_json()
The following subset of the JSONPath notation is supported:
| Path expression | Description |
|---|---|
$ | Root object |
. | Selects the specified property in a parent object. Use this notation if the property doesn’t contain special characters. |
['property'] or ["property"] | Selects the specified property in a parent object. Make sure you put single quotes or double quotes around the property name. Use this notation if the property name contains special characters, such as spaces, or begins with a character other than A..Za..z_. |
[n] | Selects the n-th element from an array. Indexes are 0-based. |
Example
Given the following JSON document:
{
"Source": "Server-01",
"Timestamp": "2023-07-25T09:15:32.123Z",
"Log Level": "INFO",
"Message": "Application started successfully.",
"Details": {
"Service": "AuthService",
"Endpoint": "/api/login",
"Response Code": 200,
"Response Time": 54.21,
"User": {
"User ID": "user123",
"Username": "kiana_anderson",
"IP Address": "192.168.1.100"
},
"Tags": [
"startup",
"auth",
"performance"
]
}
}
You can represent each of the fields with JSONPath notation as follows:
"$.Source" // Source field
"$.Timestamp" // Timestamp field
"$['Log Level']" // Log Level field
"$.Message" // Message field
"$.Details.Service" // Service field
"$.Details.Endpoint" // Endpoint field
"$.Details['Response Code']" // Response Code field
"$.Details['Response Time']" // Response Time field
"$.Details.User['User ID']" // User ID field
"$.Details.User.Username" // Username field
"$.Details.User['IP Address']" // IP Address field
"$.Tags[0]" // First value in the array of the Tags
Related content
3 - KQL docs navigation guide
KQL behavior can vary across services. On Microsoft Learn, the selected service name appears above the table of contents (TOC) under the Version dropdown. To view behavior for another service, use the Version dropdown to switch services.
Change service selection
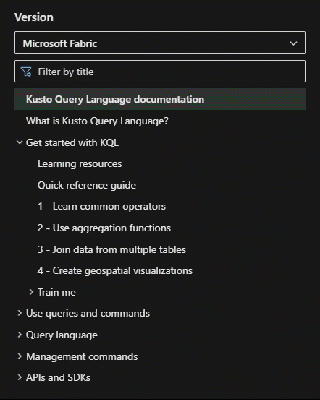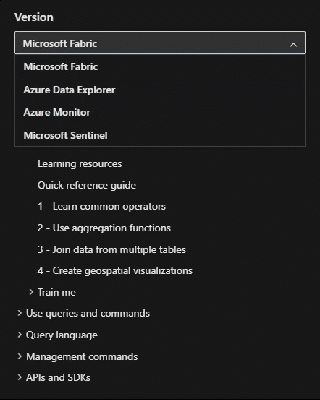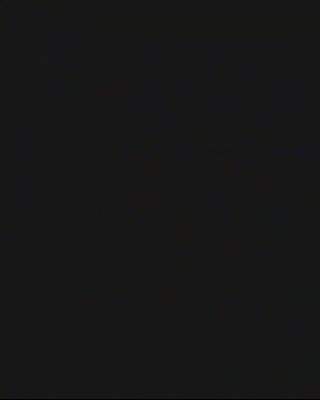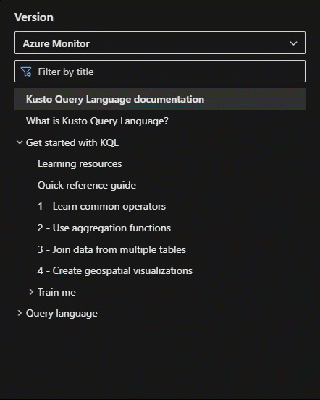
HTTPS view= parameter
Applies to services
Most KQL articles include Applies to under the title. The line lists services and shows which ones the article applies to. For example, a function might apply to Microsoft Fabric and Azure Data Explorer, but not to Azure Monitor. If you don’t see your service, the article likely doesn’t apply.
Versions
This table describes KQL versions and their associated services.
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Fabric | Microsoft Fabric is an end-to-end analytics and data platform for enterprises that need a unified solution. It covers data movement, processing, ingestion, transformation, real-time event routing, and report building. Within the suite of experiences in Microsoft Fabric, Real-Time Intelligence lets everyone in your organization extract insights and visualize streaming data. It provides an end-to-end solution for event-driven scenarios, streaming data, and data logs. The main query environment for KQL in Microsoft Fabric is the KQL queryset. KQL in Microsoft Fabric supports query operators, functions, and management commands. |
| Azure Data Explorer | Azure Data Explorer is a fully managed, high-performance analytics platform for near real-time analysis of large data volumes. Use several query environments and integrations, including the web UI. KQL in Azure Data Explorer is the full native version. It supports all query operators, functions, and management commands. |
| Azure Monitor | Log Analytics is a tool in the Azure portal you use to edit and run log queries against data in the Azure Monitor Logs store. Use Log Analytics in a Log Analytics workspace in the Azure portal. KQL in Azure Monitor uses a subset of KQL operators and functions. |
| Microsoft Sentinel | Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) platform with security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR). It provides threat detection, investigation, response, and proactive hunting across your enterprise. It uses Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspaces to store its data. KQL in Microsoft Sentinel uses a subset of KQL operators and functions. |
4 - Regex syntax
This article provides an overview of regular expression syntax supported by Kusto Query Language (KQL).
There are a number of KQL operators and functions that perform string matching, selection, and extraction with regular expressions, such as matches regex, parse, and replace_regex().
In KQL, regular expressions must be encoded as string literals and follow the string quoting rules. For example, the regular expression \A is represented in KQL as "\\A". The extra backslash indicates that the other backslash is part of the regular expression \A.
Syntax
The following sections document the regular expression syntax supported by Kusto.
Match one character
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
. | Any character except new line (includes new line with s flag). |
[0-9] | Any ASCII digit. |
[^0-9] | Any character that isn’t an ASCII digit. |
\d | Digit (\p{Nd}). |
\D | Not a digit. |
\pX | Unicode character class identified by a one-letter name. |
\p{Greek} | Unicode character class (general category or script). |
\PX | Negated Unicode character class identified by a one-letter name. |
\P{Greek} | Negated Unicode character class (general category or script). |
Character classes
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
[xyz] | Character class matching either x, y or z (union). |
[^xyz] | Character class matching any character except x, y, and z. |
[a-z] | Character class matching any character in range a-z. |
[[:alpha:]] | ASCII character class ([A-Za-z]). |
[[:^alpha:]] | Negated ASCII character class ([^A-Za-z]). |
[x[^xyz]] | Nested/grouping character class (matching any character except y and z). |
[a-y&&xyz] | Intersection (matching x or y). |
[0-9&&[^4]] | Subtraction using intersection and negation (matching 0-9 except 4). |
[0-9--4] | Direct subtraction (matching 0-9 except 4). |
[a-g~~b-h] | Symmetric difference (matching a and h only). |
[\[\]] | Escape in character classes (matching [ or ]). |
[a&&b] | Empty character class matching nothing. |
Precedence in character classes is from most binding to least binding:
- Ranges:
[a-cd]==[[a-c]d] - Union:
[ab&&bc]==[[ab]&&[bc]] - Intersection, difference, symmetric difference: All have equivalent precedence, and are evaluated from left-to-right. For example,
[\pL--\p{Greek}&&\p{Uppercase}]==[[\pL--\p{Greek}]&&\p{Uppercase}]. - Negation:
[^a-z&&b]==[^[a-z&&b]].
Composites
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
xy | Concatenation (x followed by y) |
x|y | Alternation (x or y , prefer x) |
Repetitions
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
x* | Zero or more of x (greedy) |
x+ | One or more of x (greedy) |
x? | Zero or one of x (greedy) |
x*? | Zero or more of x (ungreedy/lazy) |
x+? | One or more of x (ungreedy/lazy) |
x?? | Zero or one of x (ungreedy/lazy) |
x{n,m} | At least n x and at most m x (greedy) |
x{n,} | At least n x (greedy) |
x{n} | Exactly n x |
x{n,m}? | At least n x and at most m x (ungreedy/lazy) |
x{n,}? | At least n x (ungreedy/lazy) |
x{n}? | Exactly n x |
Empty matches
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
^ | Beginning of a haystack or start-of-line with multi-line mode. |
$ | End of a haystack or end-of-line with multi-line mode. |
\A | Only the beginning of a haystack, even with multi-line mode enabled. |
\z | Only the end of a haystack, even with multi-line mode enabled. |
\b | Unicode word boundary with \w on one side and \W, \A, or \z on other. |
\B | Not a Unicode word boundary. |
\b{start}, \< | Unicode start-of-word boundary with \W|\A at the start of the string and \w on the other side. |
\b{end}, \> | Unicode end-of-word boundary with \w on one side and \W|\z at the end. |
\b{start-half} | Half of a Unicode start-of-word boundary with \W|\A at the beginning of the boundary. |
\b{end-half} | Half of a Unicode end-of-word boundary with \W|\z at the end. |
Grouping and flags
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
(exp) | Numbered capture group (indexed by opening parenthesis). |
(?P<name>exp) | Named capture group (names must be alpha-numeric). |
(?<name>exp) | Named capture group (names must be alpha-numeric). |
(?:exp) | Non-capturing group. |
(?flags) | Set flags within current group. |
(?flags:exp) | Set flags for exp (non-capturing). |
Capture group names can contain only alpha-numeric Unicode codepoints, dots ., underscores _, and square brackets[ and ]. Names must start with either an _ or an alphabetic codepoint. Alphabetic codepoints correspond to the Alphabetic Unicode property, while numeric codepoints correspond to the union of the Decimal_Number, Letter_Number and Other_Number general categories.
Flags are single characters. For example, (?x) sets the flag x and (?-x) clears the flag x. Multiple flags can be set or cleared at the same time: (?xy) sets both the x and y flags and (?x-y) sets the x flag and clears the y flag. By default all flags are disabled unless stated otherwise. They are:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
i | Case-insensitive: letters match both upper and lower case. |
m | Multi-line mode: ^ and $ match begin/end of line. |
s | Allow dot (.). to match \n. |
R | Enables CRLF mode: when multi-line mode is enabled, \r\n is used. |
U | Swap the meaning of x* and x*?. |
u | Unicode support (enabled by default). |
x | Verbose mode, ignores whitespace and allow line comments (starting with #). |
In verbose mode, whitespace is ignored everywhere, including within character classes. To insert whitespace, use its escaped form or a hex literal. For example, \ or \x20 for an ASCII space.
Escape sequences
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
\* | Literal *, applies to all ASCII except [0-9A-Za-z<>] |
\a | Bell (\x07) |
\f | Form feed (\x0C) |
\t | Horizontal tab |
\n | New line |
\r | Carriage return |
\v | Vertical tab (\x0B) |
\A | Matches at the beginning of a haystack |
\z | Matches at the end of a haystack |
\b | Word boundary assertion |
\B | Negated word boundary assertion |
\b{start}, \< | Start-of-word boundary assertion |
\b{end}, \> | End-of-word boundary assertion |
\b{start-half} | Half of a start-of-word boundary assertion |
\b{end-half} | Half of an end-of-word boundary assertion |
\123 | Octal character code, up to three digits |
\x7F | Hex character code (exactly two digits) |
\x{10FFFF} | Hex character code corresponding to a Unicode code point |
\u007F | Hex character code (exactly four digits) |
\u{7F} | Hex character code corresponding to a Unicode code point |
\U0000007F | Hex character code (exactly eight digits) |
\U{7F} | Hex character code corresponding to a Unicode code point |
\p{Letter} | Unicode character class |
\P{Letter} | Negated Unicode character class |
\d, \s, \w | Perl character class |
\D, \S, \W | Negated Perl character class |
Perl character classes (Unicode friendly)
These classes are based on the definitions provided in UTS#18:
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
\d | Ddigit (\p{Nd}) |
\D | Not digit |
\s | Whitespace (\p{White_Space}) |
\S | Not whitespace |
\w | Word character (\p{Alphabetic} + \p{M} + \d + \p{Pc} + \p{Join_Control}) |
\W | Not word character |
ASCII character classes
These classes are based on the definitions provided in UTS#18:
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
[[:alnum:]] | Alphanumeric ([0-9A-Za-z]) |
[[:alpha:]] | Alphabetic ([A-Za-z]) |
[[:ascii:]] | ASCII ([\x00-\x7F]) |
[[:blank:]] | Blank ([\t ]) |
[[:cntrl:]] | Control ([\x00-\x1F\x7F]) |
[[:digit:]] | Digits ([0-9]) |
[[:graph:]] | Graphical ([!-~]) |
[[:lower:]] | Lower case ([a-z]) |
[[:print:]] | Printable ([ -~]) |
[[:punct:]] | Punctuation ([!-/:-@\[-`{-~]) |
[[:space:]] | Whitespace ([\t\n\v\f\r ]) |
[[:upper:]] | Upper case ([A-Z]) |
[[:word:]] | Word characters ([0-9A-Za-z_]) |
[[:xdigit:]] | Hex digit ([0-9A-Fa-f]) |
Performance
This section provides some guidance on speed and resource usage of regex expressions.
Unicode can affect memory usage and search speed
KQL regex provides first class support for Unicode. In many cases, the extra memory required to support Unicode is negligible and doesn’t typically affect search speed.
The following are some examples of Unicode character classes that can affect memory usage and search speed:
Memory usage: The effect of Unicode primarily arises from the use of Unicode character classes. Unicode character classes tend to be larger in size. For example, the
\wcharacter class matches around 140,000 distinct codepoints by default. This requires more memory and can slow down regex compilation. If ASCII satisfies your requirements, use ASCII classes instead of Unicode classes. The ASCII-only version of\wcan be expressed in multiple ways, all of which are equivalent.[0-9A-Za-z_] (?-u:\w) [[:word:]] [\w&&\p{ascii}]Search speed: Unicode tends to be handled well, even when using large Unicode character classes. However, some of the faster internal regex engines can’t handle a Unicode aware word boundary assertion. So if you don’t need Unicode-aware word boundary assertions, you might consider using
(?-u:\b)instead of\b. The(?-u:\b)uses an ASCII-only definition of a word character, which can improve search speed.
Literals can accelerate searches
KQL regex has a strong ability to recognize literals within a regex pattern, which can significantly speed up searches. If possible, including literals in your pattern can greatly improve search performance. For example, in the regex \w+@\w+, first occurrences of @ are matched and then a reverse match is performed for \w+ to find the starting position.
5 - Splunk to Kusto map
This article is intended to assist users who are familiar with Splunk learn the Kusto Query Language to write log queries with Kusto. Direct comparisons are made between the two to highlight key differences and similarities, so you can build on your existing knowledge.
Structure and concepts
The following table compares concepts and data structures between Splunk and Kusto logs:
| Concept | Splunk | Kusto | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| deployment unit | cluster | cluster | Kusto allows arbitrary cross-cluster queries. Splunk doesn’t. |
| data caches | buckets | caching and retention policies | Controls the period and caching level for the data. This setting directly affects the performance of queries and the cost of the deployment. |
| logical partition of data | index | database | Allows logical separation of the data. Both implementations allow unions and joining across these partitions. |
| structured event metadata | N/A | table | Splunk doesn’t expose the concept of event metadata to the search language. Kusto logs have the concept of a table, which has columns. Each event instance is mapped to a row. |
| record | event | row | Terminology change only. |
| record attribute | field | column | In Kusto, this setting is predefined as part of the table structure. In Splunk, each event has its own set of fields. |
| types | datatype | datatype | Kusto data types are more explicit because they’re set on the columns. Both have the ability to work dynamically with data types and roughly equivalent set of datatypes, including JSON support. |
| query and search | search | query | Concepts essentially are the same between Kusto and Splunk. |
| event ingestion time | system time | ingestion_time() | In Splunk, each event gets a system timestamp of the time the event was indexed. In Kusto, you can define a policy called ingestion_time that exposes a system column that can be referenced through the ingestion_time() function. |
Functions
The following table specifies functions in Kusto that are equivalent to Splunk functions.
| Splunk | Kusto | Comment |
|---|---|---|
strcat | strcat() | (1) |
split | split() | (1) |
if | iff() | (1) |
tonumber | todouble()tolong()toint() | (1) |
upperlower | toupper()tolower() | (1) |
replace | replace_string(), replace_strings() or replace_regex() | (1) Although replace functions take three parameters in both products, the parameters are different. |
substr | substring() | (1) Also note that Splunk uses one-based indices. Kusto notes zero-based indices. |
tolower | tolower() | (1) |
toupper | toupper() | (1) |
match | matches regex | (2) |
regex | matches regex | In Splunk, regex is an operator. In Kusto, it’s a relational operator. |
searchmatch | == | In Splunk, searchmatch allows searching for the exact string. |
random | rand() rand(n) | Splunk’s function returns a number between zero to 231-1. Kusto’s returns a number between 0.0 and 1.0, or if a parameter is provided, between 0 and n-1. |
now | now() | (1) |
relative_time | totimespan() | (1) In Kusto, Splunk’s equivalent of relative_time(datetimeVal, offsetVal) is datetimeVal + totimespan(offsetVal).For example, search | eval n=relative_time(now(), "-1d@d") becomes ... | extend myTime = now() - totimespan("1d"). |
(1) In Splunk, the function is invoked by using the eval operator. In Kusto, it’s used as part of extend or project.
(2) In Splunk, the function is invoked by using the eval operator. In Kusto, it can be used with the where operator.
Operators
The following sections give examples of how to use different operators in Splunk and Kusto.
Search
In Splunk, you can omit the search keyword and specify an unquoted string. In Kusto, you must start each query with find, an unquoted string is a column name, and the lookup value must be a quoted string.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | search | search Session.Id="c8894ffd-e684-43c9-9125-42adc25cd3fc" earliest=-24h |
| Kusto | find | find Session.Id=="c8894ffd-e684-43c9-9125-42adc25cd3fc" and ingestion_time()> ago(24h) |
Filter
Kusto log queries start from a tabular result set in which filter is applied. In Splunk, filtering is the default operation on the current index. You also can use the where operator in Splunk, but we don’t recommend it.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | search | Event.Rule="330009.2" Session.Id="c8894ffd-e684-43c9-9125-42adc25cd3fc" _indextime>-24h |
| Kusto | where | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| where Session_Id == "c8894ffd-e684-43c9-9125-42adc25cd3fc" and ingestion_time() > ago(24h) |
Get n events or rows for inspection
Kusto log queries also support take as an alias to limit. In Splunk, if the results are ordered, head returns the first n results. In Kusto, limit isn’t ordered, but it returns the first n rows that are found.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | head | Event.Rule=330009.2| head 100 |
| Kusto | limit | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| limit 100 |
Get the first n events or rows ordered by a field or column
For the bottom results, in Splunk, you use tail. In Kusto, you can specify ordering direction by using asc.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | head | Event.Rule="330009.2"| sort Event.Sequence| head 20 |
| Kusto | top | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| top 20 by Event_Sequence |
Extend the result set with new fields or columns
Splunk has an eval function, but it’s not comparable to the eval operator in Kusto. Both the eval operator in Splunk and the extend operator in Kusto support only scalar functions and arithmetic operators.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | eval | Event.Rule=330009.2| eval state= if(Data.Exception = "0", "success", "error") |
| Kusto | extend | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| extend state = iff(Data_Exception == 0,"success" ,"error") |
Rename
Kusto uses the project-rename operator to rename a field. In the project-rename operator, a query can take advantage of any indexes that are prebuilt for a field. Splunk has a rename operator that does the same.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | rename | Event.Rule=330009.2| rename Date.Exception as execption |
| Kusto | project-rename | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| project-rename exception = Date_Exception |
Format results and projection
Splunk uses the table command to select which columns to include in the results. Kusto has a project operator that does the same and more.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | table | Event.Rule=330009.2| table rule, state |
| Kusto | project | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| project exception, state |
Splunk uses the fields - command to select which columns to exclude from the results. Kusto has a project-away operator that does the same.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | fields - | Event.Rule=330009.2| fields - quota, hightest_seller |
| Kusto | project-away | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| project-away exception, state |
Aggregation
See the list of summarize aggregations functions that are available.
| Splunk operator | Splunk example | Kusto operator | Kusto example |
|---|---|---|---|
stats | search (Rule=120502.*)| stats count by OSEnv, Audience | summarize | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| summarize count() by App_Platform, Release_Audience |
evenstats | ...| stats count_i by time, category| eventstats sum(count_i) AS count_total by _time_ | join | T2| join kind=inner (T1) on _time| project _time, category, count_i, count_total |
Join
join in Splunk has substantial limitations. The subquery has a limit of 10,000 results (set in the deployment configuration file), and a limited number of join flavors are available.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | join | Event.Rule=120103* | stats by Client.Id, Data.Alias| join Client.Id max=0 [search earliest=-24h Event.Rule="150310.0" Data.Hresult=-2147221040] |
| Kusto | join | cluster("OAriaPPT").database("Office PowerPoint").Office_PowerPoint_PPT_Exceptions| where Data_Hresult== -2147221040| join kind = inner (Office_System_SystemHealthMetadata| summarize by Client_Id, Data_Alias)on Client_Id |
Sort
The default sort order is ascending. To specify descending order, add a minus sign (-) before the field name. Kusto also supports defining where to put nulls, either at the beginning or at the end.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | sort | Event.Rule=120103| sort -Data.Hresult |
| Kusto | order by | Office_Hub_OHubBGTaskError| order by Data_Hresult, desc |
Multivalue expand
The multivalue expand operator is similar in both Splunk and Kusto.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | mvexpand | mvexpand solutions |
| Kusto | mv-expand | mv-expand solutions |
Result facets, interesting fields
In Log Analytics in the Azure portal, only the first column is exposed. All columns are available through the API.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | fields | Event.Rule=330009.2| fields App.Version, App.Platform |
| Kusto | facets | Office_Excel_BI_PivotTableCreate| facet by App_Branch, App_Version |
Deduplicate
In Kusto, you can use summarize arg_min() to reverse the order of which record is chosen.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | dedup | Event.Rule=330009.2| dedup device_id sortby -batterylife |
| Kusto | summarize arg_max() | Office_Excel_BI_PivotTableCreate| summarize arg_max(batterylife, *) by device_id |
Timechart
Kusto and Splunk both use the timechart operator to visualize data over time. In Splunk, it aggregates data over specified time intervals and can be used with various statistical functions. In Kusto, the equivalent is achieved using the summarize and bin functions, followed by the render timechart operator.
| Product | Operator | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | timechart | index=StormEvents| where StartTime >= "2007-01-01" AND StartTime <= "2007-12-31" AND DamageCrops > 0| bin span=7d StartTime| stats count as EventCount by StartTime| timechart span=7d count as EventCount |
| Kusto | timechart | StormEvents| where StartTime between (datetime(2007-01-01) .. datetime(2007-12-31)) and DamageCrops > 0| summarize EventCount = count() by bin(StartTime, 7d)| render timechart |
Related content
- Walk through a tutorial on the Kusto Query Language.
6 - SQL to Kusto query translation
If you’re familiar with SQL and want to learn KQL, translate SQL queries into KQL by prefacing the SQL query with a comment line, --, and the keyword explain. The output shows the KQL version of the query, which can help you understand the KQL syntax and concepts.
--
explain
SELECT COUNT_BIG(*) as C FROM StormEvents
Output
| Query |
|---|
StormEvents<br>| summarize C=count()<br>| project C |
SQL to Kusto cheat sheet
The following table shows sample queries in SQL and their KQL equivalents.
| Category | SQL Query | Kusto Query | Learn more |
|–|–|–|
| Select data from table | SELECT * FROM dependencies | dependencies | Tabular expression statements |
|–| SELECT name, resultCode FROM dependencies | dependencies | project name, resultCode | project |
|–| SELECT TOP 100 * FROM dependencies | dependencies | take 100 | take |
| Null evaluation | SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE resultCode IS NOT NULL | dependencies| where isnotnull(resultCode) | isnotnull() |
| Comparison operators (date) | SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE timestamp > getdate()-1 | dependencies| where timestamp > ago(1d) | ago() |
|–| SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE timestamp BETWEEN ... AND ... | dependencies| where timestamp between (datetime(2016-10-01) .. datetime(2016-11-01)) | between |
| Comparison operators (string) | SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE type = "Azure blob" | dependencies| where type == "Azure blob" | Logical operators |
|–| -- substringSELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE type like "%blob%" | // substringdependencies| where type has "blob" | has |
|–| -- wildcardSELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE type like "Azure%" | // wildcarddependencies| where type startswith "Azure"// ordependencies| where type matches regex "^Azure.*" | startswithmatches regex |
| Comparison (boolean) | SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE !(success) | dependencies| where success == False | Logical operators |
| Grouping, Aggregation | SELECT name, AVG(duration) FROM dependenciesGROUP BY name | dependencies| summarize avg(duration) by name | summarizeavg() |
| Distinct | SELECT DISTINCT name, type FROM dependencies | dependencies| distinct name, type | summarizedistinct |
|–| SELECT name, COUNT(DISTINCT type)FROM dependenciesGROUP BY name | dependencies| summarize by name, type | summarize count() by name// or approximate for large setsdependencies| summarize dcount(type) by name | count()dcount() |
| Column aliases, Extending | SELECT operationName as Name, AVG(duration) as AvgD FROM dependenciesGROUP BY name | dependencies| summarize AvgD = avg(duration) by Name=operationName | Alias statement |
|–| SELECT conference, CONCAT(sessionid, ' ' , session_title) AS session FROM ConferenceSessions | ConferenceSessions| extend session=strcat(sessionid, " ", session_title)| project conference, session | strcat()project |
| Ordering | SELECT name, timestamp FROM dependenciesORDER BY timestamp ASC | dependencies| project name, timestamp| sort by timestamp asc nulls last | sort |
| Top n by measure | SELECT TOP 100 name, COUNT(*) as Count FROM dependenciesGROUP BY nameORDER BY Count DESC | dependencies| summarize Count = count() by name| top 100 by Count desc | top |
| Union | SELECT * FROM dependenciesUNIONSELECT * FROM exceptions | union dependencies, exceptions | union |
|–| SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE timestamp > ...UNIONSELECT * FROM exceptionsWHERE timestamp > ... | dependencies| where timestamp > ago(1d)| union(exceptions| where timestamp > ago(1d)) | |
| Join | SELECT * FROM dependenciesLEFT OUTER JOIN exceptionsON dependencies.operation_Id = exceptions.operation_Id | dependencies| join kind = leftouter(exceptions)on $left.operation_Id == $right.operation_Id | join |
| Nested queries | SELECT * FROM dependenciesWHERE resultCode ==(SELECT TOP 1 resultCode FROM dependenciesWHERE resultId = 7ORDER BY timestamp DESC) | dependencies| where resultCode == toscalar(dependencies| where resultId == 7| top 1 by timestamp desc| project resultCode) | toscalar |
| Having | SELECT COUNT(\*) FROM dependenciesGROUP BY nameHAVING COUNT(\*) > 3 | dependencies| summarize Count = count() by name| where Count > 3 | summarizewhere |
Related content
- Use T-SQL to query data
7 - Timezone
The following is a list of timezones supported by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Time Zone Database.
Related functions:
| Timezone |
|---|
| Africa/Abidjan |
| Africa/Accra |
| Africa/Addis_Ababa |
| Africa/Algiers |
| Africa/Asmara |
| Africa/Asmera |
| Africa/Bamako |
| Africa/Bangui |
| Africa/Banjul |
| Africa/Bissau |
| Africa/Blantyre |
| Africa/Brazzaville |
| Africa/Bujumbura |
| Africa/Cairo |
| Africa/Casablanca |
| Africa/Ceuta |
| Africa/Conakry |
| Africa/Dakar |
| Africa/Dar_es_Salaam |
| Africa/Djibouti |
| Africa/Douala |
| Africa/El_Aaiun |
| Africa/Freetown |
| Africa/Gaborone |
| Africa/Harare |
| Africa/Johannesburg |
| Africa/Juba |
| Africa/Kampala |
| Africa/Khartoum |
| Africa/Kigali |
| Africa/Kinshasa |
| Africa/Lagos |
| Africa/Libreville |
| Africa/Lome |
| Africa/Luanda |
| Africa/Lubumbashi |
| Africa/Lusaka |
| Africa/Malabo |
| Africa/Maputo |
| Africa/Maseru |
| Africa/Mbabane |
| Africa/Mogadishu |
| Africa/Monrovia |
| Africa/Nairobi |
| Africa/Ndjamena |
| Africa/Niamey |
| Africa/Nouakchott |
| Africa/Ouagadougou |
| Africa/Porto-Novo |
| Africa/Sao_Tome |
| Africa/Timbuktu |
| Africa/Tripoli |
| Africa/Tunis |
| Africa/Windhoek |
| America/Adak |
| America/Anchorage |
| America/Anguilla |
| America/Antigua |
| America/Araguaina |
| America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires |
| America/Argentina/Catamarca |
| America/Argentina/ComodRivadavia |
| America/Argentina/Cordoba |
| America/Argentina/Jujuy |
| America/Argentina/La_Rioja |
| America/Argentina/Mendoza |
| America/Argentina/Rio_Gallegos |
| America/Argentina/Salta |
| America/Argentina/San_Juan |
| America/Argentina/San_Luis |
| America/Argentina/Tucuman |
| America/Argentina/Ushuaia |
| America/Aruba |
| America/Asuncion |
| America/Atikokan |
| America/Atka |
| America/Bahia |
| America/Bahia_Banderas |
| America/Barbados |
| America/Belem |
| America/Belize |
| America/Blanc-Sablon |
| America/Boa_Vista |
| America/Bogota |
| America/Boise |
| America/Buenos_Aires |
| America/Cambridge_Bay |
| America/Campo_Grande |
| America/Cancun |
| America/Caracas |
| America/Catamarca |
| America/Cayenne |
| America/Cayman |
| America/Chicago |
| America/Chihuahua |
| America/Coral_Harbour |
| America/Cordoba |
| America/Costa_Rica |
| America/Creston |
| America/Cuiaba |
| America/Curacao |
| America/Danmarkshavn |
| America/Dawson |
| America/Dawson_Creek |
| America/Denver |
| America/Detroit |
| America/Dominica |
| America/Edmonton |
| America/Eirunepe |
| America/El_Salvador |
| America/Ensenada |
| America/Fort_Nelson |
| America/Fort_Wayne |
| America/Fortaleza |
| America/Glace_Bay |
| America/Godthab |
| America/Goose_Bay |
| America/Grand_Turk |
| America/Grenada |
| America/Guadeloupe |
| America/Guatemala |
| America/Guayaquil |
| America/Guyana |
| America/Halifax |
| America/Havana |
| America/Hermosillo |
| America/Indiana/Indianapolis |
| America/Indiana/Knox |
| America/Indiana/Marengo |
| America/Indiana/Petersburg |
| America/Indiana/Tell_City |
| America/Indiana/Vevay |
| America/Indiana/Vincennes |
| America/Indiana/Winamac |
| America/Indianapolis |
| America/Inuvik |
| America/Iqaluit |
| America/Jamaica |
| America/Jujuy |
| America/Juneau |
| America/Kentucky/Louisville |
| America/Kentucky/Monticello |
| America/Knox_IN |
| America/Kralendijk |
| America/La_Paz |
| America/Lima |
| America/Los_Angeles |
| America/Louisville |
| America/Lower_Princes |
| America/Maceio |
| America/Managua |
| America/Manaus |
| America/Marigot |
| America/Martinique |
| America/Matamoros |
| America/Mazatlan |
| America/Mendoza |
| America/Menominee |
| America/Merida |
| America/Metlakatla |
| America/Mexico_City |
| America/Miquelon |
| America/Moncton |
| America/Monterrey |
| America/Montevideo |
| America/Montreal |
| America/Montserrat |
| America/Nassau |
| America/New_York |
| America/Nipigon |
| America/Nome |
| America/Noronha |
| America/North_Dakota/Beulah |
| America/North_Dakota/Center |
| America/North_Dakota/New_Salem |
| America/Nuuk |
| America/Ojinaga |
| America/Panama |
| America/Pangnirtung |
| America/Paramaribo |
| America/Phoenix |
| America/Port-au-Prince |
| America/Port_of_Spain |
| America/Porto_Acre |
| America/Porto_Velho |
| America/Puerto_Rico |
| America/Punta_Arenas |
| America/Rainy_River |
| America/Rankin_Inlet |
| America/Recife |
| America/Regina |
| America/Resolute |
| America/Rio_Branco |
| America/Rosario |
| America/Santa_Isabel |
| America/Santarem |
| America/Santiago |
| America/Santo_Domingo |
| America/Sao_Paulo |
| America/Scoresbysund |
| America/Shiprock |
| America/Sitka |
| America/St_Barthelemy |
| America/St_Johns |
| America/St_Kitts |
| America/St_Lucia |
| America/St_Thomas |
| America/St_Vincent |
| America/Swift_Current |
| America/Tegucigalpa |
| America/Thule |
| America/Thunder_Bay |
| America/Tijuana |
| America/Toronto |
| America/Tortola |
| America/Vancouver |
| America/Virgin |
| America/Whitehorse |
| America/Winnipeg |
| America/Yakutat |
| America/Yellowknife |
| Antarctica/Casey |
| Antarctica/Davis |
| Antarctica/DumontDUrville |
| Antarctica/Macquarie |
| Antarctica/Mawson |
| Antarctica/McMurdo |
| Antarctica/Palmer |
| Antarctica/Rothera |
| Antarctica/South_Pole |
| Antarctica/Syowa |
| Antarctica/Troll |
| Antarctica/Vostok |
| Arctic/Longyearbyen |
| Asia/Aden |
| Asia/Almaty |
| Asia/Amman |
| Asia/Anadyr |
| Asia/Aqtau |
| Asia/Aqtobe |
| Asia/Ashgabat |
| Asia/Ashkhabad |
| Asia/Atyrau |
| Asia/Baghdad |
| Asia/Bahrain |
| Asia/Baku |
| Asia/Bangkok |
| Asia/Barnaul |
| Asia/Beirut |
| Asia/Bishkek |
| Asia/Brunei |
| Asia/Kolkata |
| Asia/Chita |
| Asia/Choibalsan |
| Asia/Chongqing |
| Asia/Colombo |
| Asia/Dacca |
| Asia/Damascus |
| Asia/Dhaka |
| Asia/Dili |
| Asia/Dubai |
| Asia/Dushanbe |
| Asia/Famagusta |
| Asia/Gaza |
| Asia/Harbin |
| Asia/Hebron |
| Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh_City |
| Asia/Hong_Kong |
| Asia/Hovd |
| Asia/Irkutsk |
| Asia/Istanbul |
| Asia/Jakarta |
| Asia/Jayapura |
| Asia/Jerusalem |
| Asia/Kabul |
| Asia/Kamchatka |
| Asia/Karachi |
| Asia/Kashgar |
| Asia/Kathmandu |
| Asia/Katmandu |
| Asia/Khandyga |
| Asia/Kolkata |
| Asia/Krasnoyarsk |
| Asia/Kuala_Lumpur |
| Asia/Kuching |
| Asia/Kuwait |
| Asia/Macao Special Administrative Region |
| Asia/Magadan |
| Asia/Makassar |
| Asia/Manila |
| Asia/Muscat |
| Asia/Nicosia |
| Asia/Novokuznetsk |
| Asia/Novosibirsk |
| Asia/Omsk |
| Asia/Oral |
| Asia/Phnom_Penh |
| Asia/Pontianak |
| Asia/Pyongyang |
| Asia/Qatar |
| Asia/Qostanay |
| Asia/Qyzylorda |
| Asia/Yangon (Rangoon) |
| Asia/Riyadh |
| Asia/Sakhalin |
| Asia/Samarkand |
| Asia/Seoul |
| Asia/Shanghai |
| Asia/Singapore |
| Asia/Srednekolymsk |
| Asia/Taipei |
| Asia/Tashkent |
| Asia/Tbilisi |
| Asia/Tehran |
| Asia/Tel_Aviv |
| Asia/Thimbu |
| Asia/Thimphu |
| Asia/Tokyo |
| Asia/Tomsk |
| Asia/Ujung_Pandang |
| Asia/Ulaanbaatar |
| Asia/Ulan_Bator |
| Asia/Urumqi |
| Asia/Ust-Nera |
| Asia/Vientiane |
| Asia/Vladivostok |
| Asia/Yakutsk |
| Asia/Yangon |
| Asia/Yekaterinburg |
| Asia/Yerevan |
| Atlantic/Azores |
| Atlantic/Bermuda |
| Atlantic/Canary |
| Atlantic/Cape_Verde |
| Atlantic/Faeroe |
| Atlantic/Faroe |
| Atlantic/Jan_Mayen |
| Atlantic/Madeira |
| Atlantic/Reykjavik |
| Atlantic/South_Georgia |
| Atlantic/St_Helena |
| Atlantic/Stanley |
| Australia/ACT |
| Australia/Adelaide |
| Australia/Brisbane |
| Australia/Broken_Hill |
| Australia/Canberra |
| Australia/Currie |
| Australia/Darwin |
| Australia/Eucla |
| Australia/Hobart |
| Australia/LHI |
| Australia/Lindeman |
| Australia/Lord_Howe |
| Australia/Melbourne |
| Australia/NSW |
| Australia/North |
| Australia/Perth |
| Australia/Queensland |
| Australia/South |
| Australia/Sydney |
| Australia/Tasmania |
| Australia/Victoria |
| Australia/West |
| Australia/Yancowinna |
| Brazil/Acre |
| Brazil/DeNoronha |
| Brazil/East |
| Brazil/West |
| CET |
| CST6CDT |
| Canada/Atlantic |
| Canada/Central |
| Canada/Eastern |
| Canada/Mountain |
| Canada/Newfoundland and Labrador |
| Canada/Pacific |
| Canada/Saskatchewan |
| Canada/Yukon |
| Chile/Continental |
| Chile/EasterIsland |
| Cuba |
| EET |
| EST |
| EST5EDT |
| Egypt |
| Eire |
| Etc/GMT |
| Etc/GMT+0 |
| Etc/GMT+1 |
| Etc/GMT+10 |
| Etc/GMT+11 |
| Etc/GMT+12 |
| Etc/GMT+2 |
| Etc/GMT+3 |
| Etc/GMT+4 |
| Etc/GMT+5 |
| Etc/GMT+6 |
| Etc/GMT+7 |
| Etc/GMT+8 |
| Etc/GMT+9 |
| Etc/GMT-0 |
| Etc/GMT-1 |
| Etc/GMT-10 |
| Etc/GMT-11 |
| Etc/GMT-12 |
| Etc/GMT-13 |
| Etc/GMT-14 |
| Etc/GMT-2 |
| Etc/GMT-3 |
| Etc/GMT-4 |
| Etc/GMT-5 |
| Etc/GMT-6 |
| Etc/GMT-7 |
| Etc/GMT-8 |
| Etc/GMT-9 |
| Etc/GMT0 |
| Etc/Greenwich |
| Etc/UCT |
| Etc/UTC |
| Etc/Universal |
| Etc/Zulu |
| Europe/Amsterdam |
| Europe/Andorra |
| Europe/Astrakhan |
| Europe/Athens |
| Europe/Belfast |
| Europe/Belgrade |
| Europe/Berlin |
| Europe/Bratislava |
| Europe/Brussels |
| Europe/Bucharest |
| Europe/Budapest |
| Europe/Busingen |
| Europe/Chisinau |
| Europe/Copenhagen |
| Europe/Dublin |
| Europe/Gibraltar |
| Europe/Guernsey |
| Europe/Helsinki |
| Europe/Isle_of_Man |
| Europe/Istanbul |
| Europe/Jersey |
| Europe/Kaliningrad |
| Europe/Kyiv |
| Europe/Kirov |
| Europe/Lisbon |
| Europe/Ljubljana |
| Europe/London |
| Europe/Luxembourg |
| Europe/Madrid |
| Europe/Malta |
| Europe/Mariehamn |
| Europe/Minsk |
| Europe/Monaco |
| Europe/Moscow |
| Europe/Nicosia |
| Europe/Oslo |
| Europe/Paris |
| Europe/Podgorica |
| Europe/Prague |
| Europe/Riga |
| Europe/Rome |
| Europe/Samara |
| Europe/San_Marino |
| Europe/Sarajevo |
| Europe/Saratov |
| Europe/Simferopol |
| Europe/Skopje |
| Europe/Sofia |
| Europe/Stockholm |
| Europe/Tallinn |
| Europe/Tirane |
| Europe/Tiraspol |
| Europe/Ulyanovsk |
| Europe/Uzhgorod |
| Europe/Vaduz |
| Europe/Vatican |
| Europe/Vienna |
| Europe/Vilnius |
| Europe/Volgograd |
| Europe/Warsaw |
| Europe/Zagreb |
| Europe/Zaporozhye |
| Europe/Zurich |
| GB |
| GB-Eire |
| GMT |
| GMT+0 |
| GMT-0 |
| GMT0 |
| Greenwich |
| HST |
| Hongkong |
| Iceland |
| Indian/Antananarivo |
| Indian/Chagos |
| Indian/Christmas |
| Indian/Cocos |
| Indian/Comoro |
| Indian/Kerguelen |
| Indian/Mahe |
| Indian/Maldives |
| Indian/Mauritius |
| Indian/Mayotte |
| Indian/Reunion |
| Iran |
| Israel |
| Jamaica |
| Japan |
| Kwajalein |
| Libya |
| MET |
| MST |
| MST7MDT |
| Mexico/BajaNorte |
| Mexico/BajaSur |
| Mexico/General |
| NZ |
| NZ-CHAT |
| Navajo |
| PRC |
| PST8PDT |
| Pacific/Apia |
| Pacific/Auckland |
| Pacific/Bougainville |
| Pacific/Chatham |
| Pacific/Chuuk |
| Pacific/Easter |
| Pacific/Efate |
| Pacific/Enderbury |
| Pacific/Fakaofo |
| Pacific/Fiji |
| Pacific/Funafuti |
| Pacific/Galapagos |
| Pacific/Gambier |
| Pacific/Guadalcanal |
| Pacific/Guam |
| Pacific/Honolulu |
| Pacific/Johnston |
| Pacific/Kanton |
| Pacific/Kiritimati |
| Pacific/Kosrae |
| Pacific/Kwajalein |
| Pacific/Majuro |
| Pacific/Marquesas |
| Pacific/Midway |
| Pacific/Nauru |
| Pacific/Niue |
| Pacific/Norfolk |
| Pacific/Noumea |
| Pacific/Pago_Pago |
| Pacific/Palau |
| Pacific/Pitcairn |
| Pacific/Pohnpei |
| Pacific/Ponape |
| Pacific/Port_Moresby |
| Pacific/Rarotonga |
| Pacific/Saipan |
| Pacific/Samoa |
| Pacific/Tahiti |
| Pacific/Tarawa |
| Pacific/Tongatapu |
| Pacific/Truk |
| Pacific/Wake |
| Pacific/Wallis |
| Pacific/Yap |
| Poland |
| Portugal |
| ROK |
| Singapore |
| Türkiye |
| UCT |
| US/Alaska |
| US/Aleutian |
| US/Arizona |
| US/Central |
| US/East-Indiana |
| US/Eastern |
| US/Hawaii |
| US/Indiana-Starke |
| US/Michigan |
| US/Mountain |
| US/Pacific |
| US/Samoa |
| UTC |
| Universal |
| W-SU |
| WET |
| Zulu |