This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
join flavors
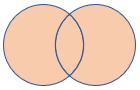
1 - fullouter join
A fullouter join combines the effect of applying both left and right outer-joins. For columns of the table that lack a matching row, the result set contains null values. For those records that do match, a single row is produced in the result set containing fields populated from both tables.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=fullouter [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from both tables, including the matching keys.
Rows: All records from both tables with unmatched cells populated with null.
Example
This example query combines rows from both tables X and Y, filling in missing values with NULL where there’s no match in the other table. This allows you to see all possible combinations of keys from both tables.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=fullouter Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 | Key1 | Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | 3 | b | 10 |
| b | 2 | b | 10 |
| c | 4 | c | 20 |
| c | 4 | c | 30 |
| d | 40 | ||
| a | 1 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
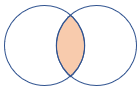
2 - inner join
The inner join flavor is like the standard inner join from the SQL world. An output record is produced whenever a record on the left side has the same join key as the record on the right side.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=inner [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from both tables, including the matching keys.
Rows: Only matching rows from both tables.
Example
The example query combines rows from tables X and Y where the keys match, showing only the rows that exist in both tables.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'k',5,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40,
'k',50
];
X | join kind=inner Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 | Key1 | Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | 3 | b | 10 |
| b | 2 | b | 10 |
| c | 4 | c | 20 |
| c | 4 | c | 30 |
| k | 5 | k | 50 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
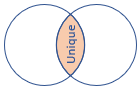
3 - innerunique join
The innerunique join flavor removes duplicate keys from the left side. This behavior ensures that the output contains a row for every combination of unique left and right keys.
By default, the innerunique join flavor is used if the kind parameter isn’t specified. This default implementation is useful in log/trace analysis scenarios, where you aim to correlate two events based on a shared correlation ID. It allows you to retrieve all instances of the phenomenon while disregarding duplicate trace records that contribute to the correlation.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=innerunique [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from both tables, including the matching keys.
Rows: All deduplicated rows from the left table that match rows from the right table.
Examples
Review the examples and run them in your Data Explorer query page.
Use the default innerunique join
The example query combines rows from tables X and Y where the keys match, showing only the rows that exist in both tables
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 | Key1 | Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | 2 | b | 10 |
| c | 4 | c | 20 |
| c | 4 | c | 30 |
The query executed the default join, which is an inner join after deduplicating the left side based on the join key. The deduplication keeps only the first record. The resulting left side of the join after deduplication is:
| Key | Value1 |
|---|---|
| a | 1 |
| b | 2 |
| c | 4 |
Two possible outputs from innerunique join
let t1 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.1",
1, "val1.2"
];
let t2 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.3",
1, "val1.4"
];
t1
| join kind = innerunique
t2
on key
Output
| key | value | key1 | value1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | val1.1 | 1 | val1.3 |
| 1 | val1.1 | 1 | val1.4 |
let t1 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.1",
1, "val1.2"
];
let t2 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.3",
1, "val1.4"
];
t1
| join kind = innerunique
t2
on key
Output
| key | value | key1 | value1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | val1.2 | 1 | val1.3 |
| 1 | val1.2 | 1 | val1.4 |
- Kusto is optimized to push filters that come after the
join, towards the appropriate join side, left or right, when possible. - Sometimes, the flavor used is innerunique and the filter is propagated to the left side of the join. The flavor is automatically propagated and the keys that apply to that filter appear in the output.
- Use the previous example and add a filter
where value == "val1.2". It gives the second result and will never give the first result for the datasets:
let t1 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.1",
1, "val1.2"
];
let t2 = datatable(key: long, value: string)
[
1, "val1.3",
1, "val1.4"
];
t1
| join kind = innerunique
t2
on key
| where value == "val1.2"
Output
| key | value | key1 | value1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | val1.2 | 1 | val1.3 |
| 1 | val1.2 | 1 | val1.4 |
Get extended sign-in activities
Get extended activities from a login that some entries mark as the start and end of an activity.
let Events = MyLogTable | where type=="Event" ;
Events
| where Name == "Start"
| project Name, City, ActivityId, StartTime=timestamp
| join (Events
| where Name == "Stop"
| project StopTime=timestamp, ActivityId)
on ActivityId
| project City, ActivityId, StartTime, StopTime, Duration = StopTime - StartTime
let Events = MyLogTable | where type=="Event" ;
Events
| where Name == "Start"
| project Name, City, ActivityIdLeft = ActivityId, StartTime=timestamp
| join (Events
| where Name == "Stop"
| project StopTime=timestamp, ActivityIdRight = ActivityId)
on $left.ActivityIdLeft == $right.ActivityIdRight
| project City, ActivityId, StartTime, StopTime, Duration = StopTime - StartTime
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
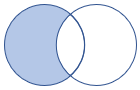
4 - leftanti join
The leftanti join flavor returns all records from the left side that don’t match any record from the right side. The anti join models the “NOT IN” query.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=leftanti [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from the left table.
Rows: All records from the left table that don’t match records from the right table.
Example
The example query combines rows from tables X and Y where there is no match in Y for the keys in X, effectively filtering out any rows in X that have corresponding rows in Y.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=leftanti Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 |
|---|---|
| a | 1 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
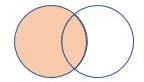
5 - leftouter join
The leftouter join flavor returns all the records from the left side table and only matching records from the right side table.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=leftouter [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from both tables, including the matching keys.
Rows: All records from the left table and only matching rows from the right table.
Example
The result of a left outer join for tables X and Y always contains all records of the left table (X), even if the join condition doesn’t find any matching record in the right table (Y).
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=leftouter Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 | Key1 | Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | ||
| b | 2 | b | 10 |
| b | 3 | b | 10 |
| c | 4 | c | 20 |
| c | 4 | c | 30 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
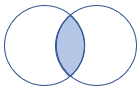
6 - leftsemi join
The leftsemi join flavor returns all records from the left side that match a record from the right side. Only columns from the left side are returned.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=leftsemi [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from the left table.
Rows: All records from the left table that match records from the right table.
Example
This query filters and returns only those rows from table X that have a matching key in table Y.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=leftsemi Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 |
|---|---|
| b | 2 |
| b | 3 |
| c | 4 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
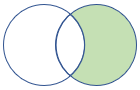
7 - rightanti join
The rightanti join flavor returns all records from the right side that don’t match any record from the left side. The anti join models the “NOT IN” query.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=rightanti [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from the right table.
Rows: All records from the right table that don’t match records from the left table.
Example
This query filters and returns only those rows from table Y that do not have a matching key in table X.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=rightanti Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 |
|---|---|
| d | 40 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
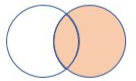
8 - rightouter join
The rightouter join flavor returns all the records from the right side and only matching records from the left side. This join flavor resembles the leftouter join flavor, but the treatment of the tables is reversed.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=rightouter [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from both tables, including the matching keys.
Rows: All records from the right table and only matching rows from the left table.
Example
This query returns all rows from table Y and any matching rows from table X, filling in NULL values where there is no match from X.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=rightouter Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value1 | Key1 | Value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | 2 | b | 10 |
| b | 3 | b | 10 |
| c | 4 | c | 20 |
| c | 4 | c | 30 |
| d | 40 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors
9 - rightsemi join
The rightsemi join flavor returns all records from the right side that match a record from the left side. Only columns from the right side are returned.
Syntax
LeftTable | join kind=rightsemi [ Hints ] RightTable on Conditions
Returns
Schema: All columns from the right table.
Rows: All records from the right table that match records from the left table.
Example
This query filters and returns only those rows from table Y that have a matching key in table X.
let X = datatable(Key:string, Value1:long)
[
'a',1,
'b',2,
'b',3,
'c',4
];
let Y = datatable(Key:string, Value2:long)
[
'b',10,
'c',20,
'c',30,
'd',40
];
X | join kind=rightsemi Y on Key
Output
| Key | Value2 |
|---|---|
| b | 10 |
| c | 20 |
| c | 30 |
Related content
- Learn about other join flavors