series_fit_2lines()
Applies a two segmented linear regression on a series, returning multiple columns.
Takes an expression containing dynamic numerical array as input and applies a two segmented linear regression in order to identify and quantify a trend change in a series. The function iterates on the series indexes. In each iteration, the function splits the series to two parts, fits a separate line (using series_fit_line()) to each part, and calculates the total r-square. The best split is the one that maximized r-square; the function returns its parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
rsquare | R-square is standard measure of the fit quality. It’s a number in the range [0-1], where 1 - is the best possible fit, and 0 means the data is unordered and don’t fit any line. |
split_idx | The index of breaking point to two segments (zero-based). |
variance | Variance of the input data. |
rvariance | Residual variance, which is the variance between the input data values the approximated ones (by the two line segments). |
line_fit | Numerical array holding a series of values of the best fitted line. The series length is equal to the length of the input array. It’s mainly used for charting. |
right_rsquare | R-square of the line on the right side of the split, see series_fit_line(). |
right_slope | Slope of the right approximated line (of the form y=ax+b). |
right_interception | Interception of the approximated left line (b from y=ax+b). |
right_variance | Variance of the input data on the right side of the split. |
right_rvariance | Residual variance of the input data on the right side of the split. |
left_rsquare | R-square of the line on the left side of the split, see series_fit_line(). |
left_slope | Slope of the left approximated line (of the form y=ax+b). |
left_interception | Interception of the approximated left line (of the form y=ax+b). |
left_variance | Variance of the input data on the left side of the split. |
left_rvariance | Residual variance of the input data on the left side of the split. |
Syntax
project series_fit_2lines(series)
- Will return all mentioned above columns with the following names: series_fit_2lines_x_rsquare, series_fit_2lines_x_split_idx etc.
project (rs, si, v)=series_fit_2lines(series)
- Will return the following columns: rs (r-square), si (split index), v (variance) and the rest will look like series_fit_2lines_x_rvariance, series_fit_2lines_x_line_fit and etc.
extend (rs, si, v)=series_fit_2lines(series)
- Will return only: rs (r-square), si (split index) and v (variance).
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| series | dynamic | ✔️ | An array of numeric values. |
Examples
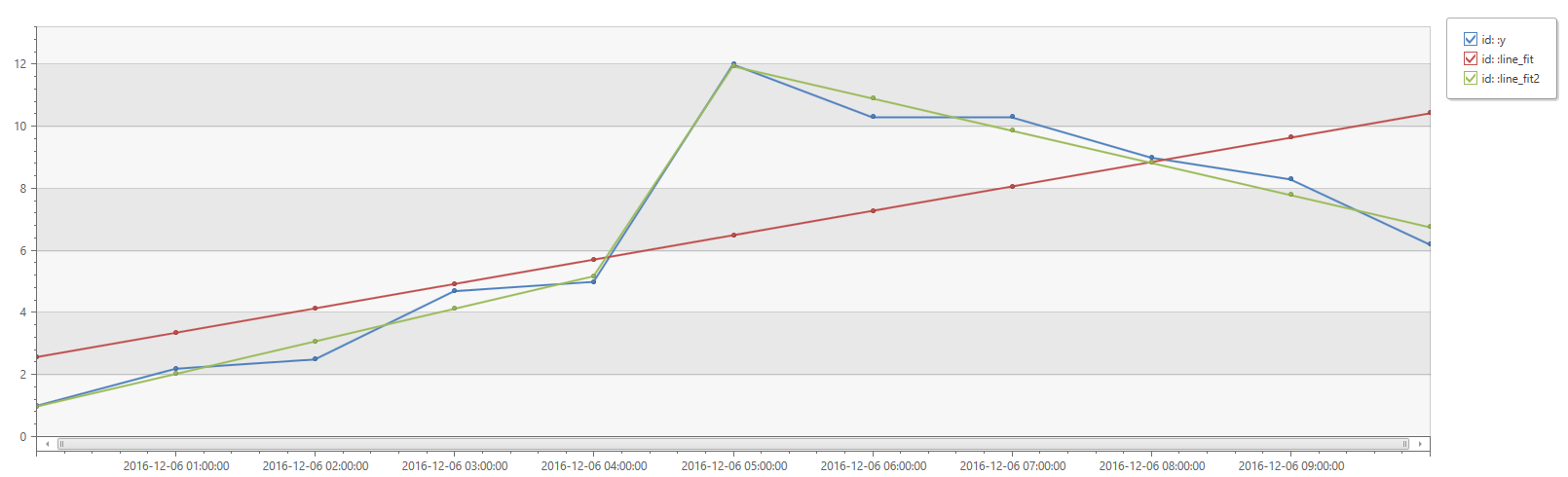
print
id=' ',
x=range(bin(now(), 1h) - 11h, bin(now(), 1h), 1h),
y=dynamic([1, 2.2, 2.5, 4.7, 5.0, 12, 10.3, 10.3, 9, 8.3, 6.2])
| extend
(Slope, Interception, RSquare, Variance, RVariance, LineFit)=series_fit_line(y),
(RSquare2, SplitIdx, Variance2, RVariance2, LineFit2)=series_fit_2lines(y)
| project id, x, y, LineFit, LineFit2
| render timechart
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.