series_fit_line()
Learn how to use the series_fit_line() function to apply a linear regression on a series to return multiple columns.
Applies linear regression on a series, returning multiple columns.
Takes an expression containing dynamic numerical array as input and does linear regression to find the line that best fits it. This function should be used on time series arrays, fitting the output of make-series operator. The function generates the following columns:
rsquare: r-square is a standard measure of the fit quality. The value’s a number in the range [0-1], where 1 - is the best possible fit, and 0 means the data is unordered and doesn’t fit any line.slope: Slope of the approximated line (“a” from y=ax+b).variance: Variance of the input data.rvariance: Residual variance that is the variance between the input data values the approximated ones.interception: Interception of the approximated line (“b” from y=ax+b).line_fit: Numerical array holding a series of values of the best fitted line. The series length is equal to the length of the input array. The value’s used for charting.
Syntax
series_fit_line(series)
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| series | dynamic | ✔️ | An array of numeric values. |
Examples
print
id=' ',
x=range(bin(now(), 1h) - 11h, bin(now(), 1h), 1h),
y=dynamic([2, 5, 6, 8, 11, 15, 17, 18, 25, 26, 30, 30])
| extend (RSquare, Slope, Variance, RVariance, Interception, LineFit)=series_fit_line(y)
| render timechart
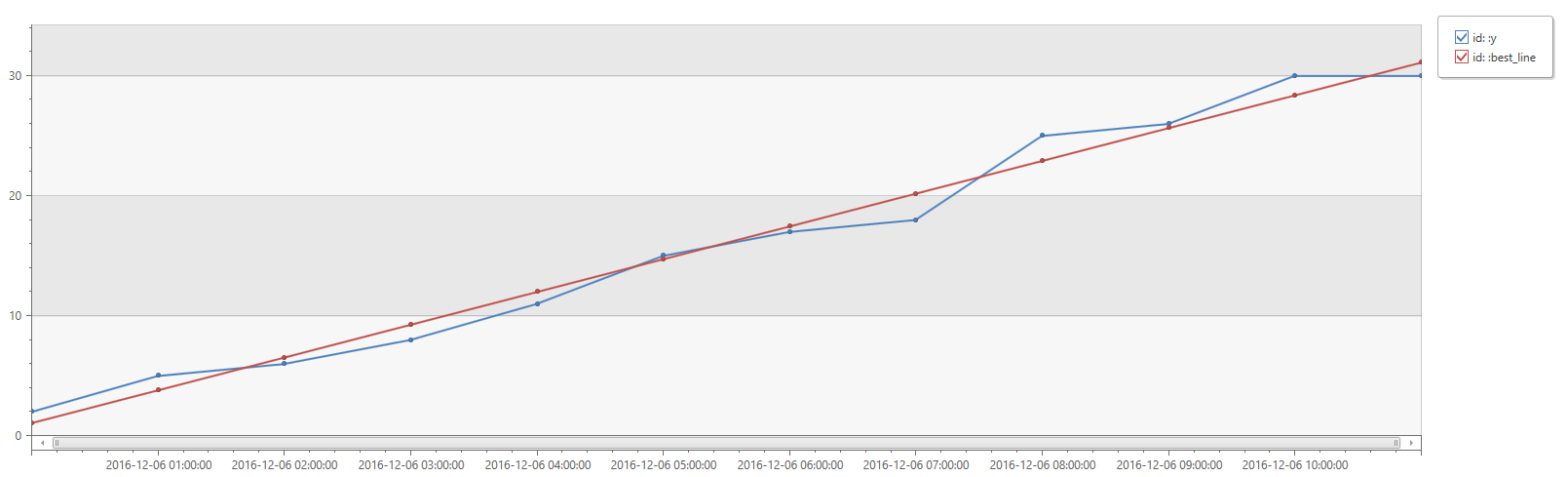
| RSquare | Slope | Variance | RVariance | Interception | LineFit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.982 | 2.730 | 98.628 | 1.686 | -1.666 | 1.064, 3.7945, 6.526, 9.256, 11.987, 14.718, 17.449, 20.180, 22.910, 25.641, 28.371, 31.102 |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.